What Does "X5R" Mean in Capacitors? A Guide to Temperature Coefficients
For beginners in the electronics industry, terms like "X5R" can be confusing when selecting capacitors. Understanding this and other common temperature coefficients can significantly enhance your ability to choose the right capacitor for your project. This article simplifies the concept and explains the key differences among popular temperature coefficients, helping procurement professionals, engineers, and enthusiasts make informed decisions.
What Does "X5R" Represent?
"X5R" is a temperature coefficient classification for multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), as defined by the EIA (Electronic Industries Alliance). It indicates how the capacitance value changes with temperature.
"X": The capacitor can operate between -55°C and +85°C.
"5": The maximum capacitance variation is ±15% within this range.
"R": Indicates the capacitor is stable and non-polarized.
This makes X5R capacitors suitable for general-purpose applications, including power supplies, filtering, and decoupling. They provide a good balance between performance, size, and cost.
Other Common Temperature Coefficients
Apart from X5R, several other temperature coefficients are widely used, each suited for different applications.
X7R
Temperature Range: -55°C to +125°C.
Capacitance Variation: ±15%.
Applications: X7R capacitors are popular in automotive and industrial applications due to their wider temperature range.
C0G (or NP0)
Temperature Range: -55°C to +125°C.
Capacitance Variation: ±30 ppm/°C (near zero change).
Applications: Known for high stability, these are ideal for precision circuits like oscillators and filters.
Y5V
Temperature Range: -30°C to +85°C.
Capacitance Variation: +22% to -82%.
Applications: Y5V capacitors are cost-effective and used in non-critical applications, such as decoupling in consumer electronics.
Z5U
Temperature Range: +10°C to +85°C.
Capacitance Variation: +22% to -56%.
Applications: Similar to Y5V, Z5U capacitors are used in low-cost, low-performance designs.
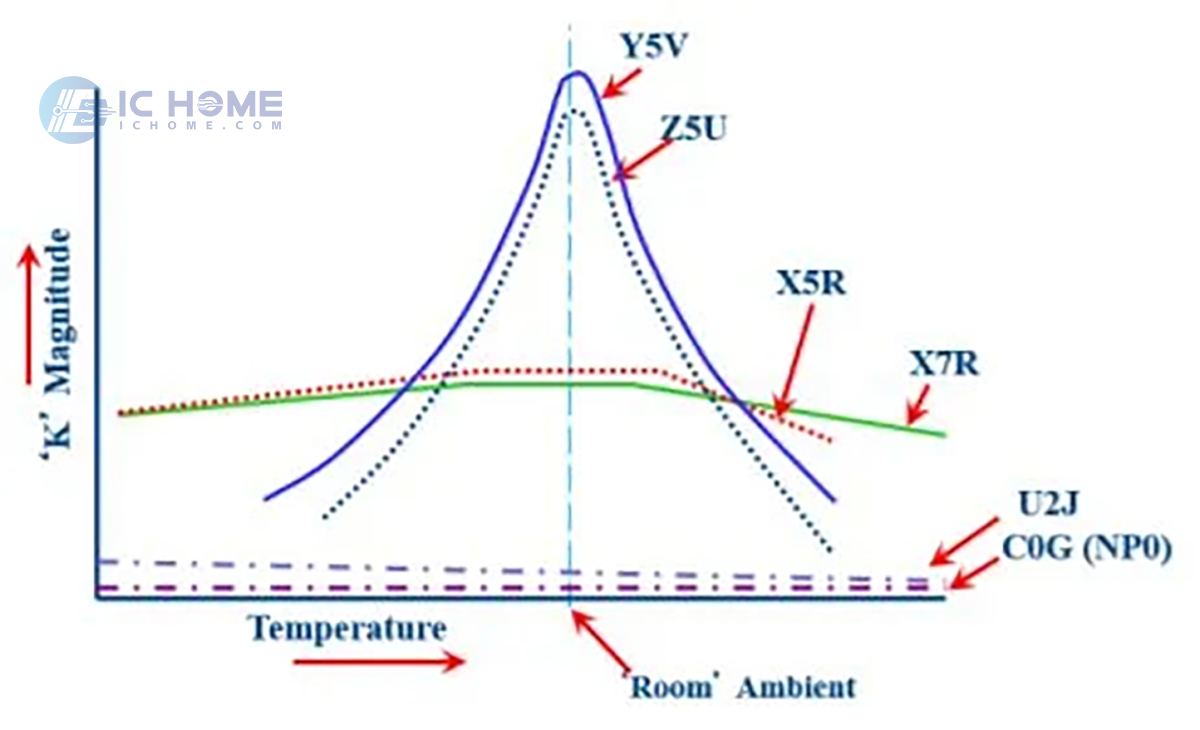
Key Differences and How to Choose
Understanding the distinctions between these coefficients can help you select the right capacitor:
Temperature Stability:
C0G/NP0 offers the best stability, suitable for sensitive applications.
X5R and X7R provide moderate stability, balancing cost and performance.
Y5V and Z5U have poor stability, making them less reliable in demanding environments.
Operating Temperature Range:
X7R is ideal for high-temperature applications, while X5R suits general use.
C0G/NP0 also works in a wide range, but with a focus on stability rather than high capacitance.
Cost and Size:
Y5V and Z5U are cheaper and smaller but have significant capacitance changes with temperature.
Conclusion
The choice of temperature coefficient, whether X5R, X7R, or others, depends on your project’s specific needs, including operating temperature, stability, and budget.
For a balanced solution, X5R capacitors are a versatile option, offering good performance for most applications. However, if precision or high-temperature performance is critical, alternatives like C0G or X7R might be more suitable.
By understanding these classifications, you can make informed decisions, ensuring reliability and efficiency in your designs. Next time you’re sourcing capacitors, keep these distinctions in mind for optimal results!
For more information or to request a quote, please feel free to send us an RFQ.
Some Model Numbers